SUBMICRON AIRBORNE DUST PARTICLE MONITORING SYSTEM
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24193/subbchem.2021.02.19Keywords:
suspended particulate matter, submicron particle monitoring, air quality, analytical instrumentation.Abstract
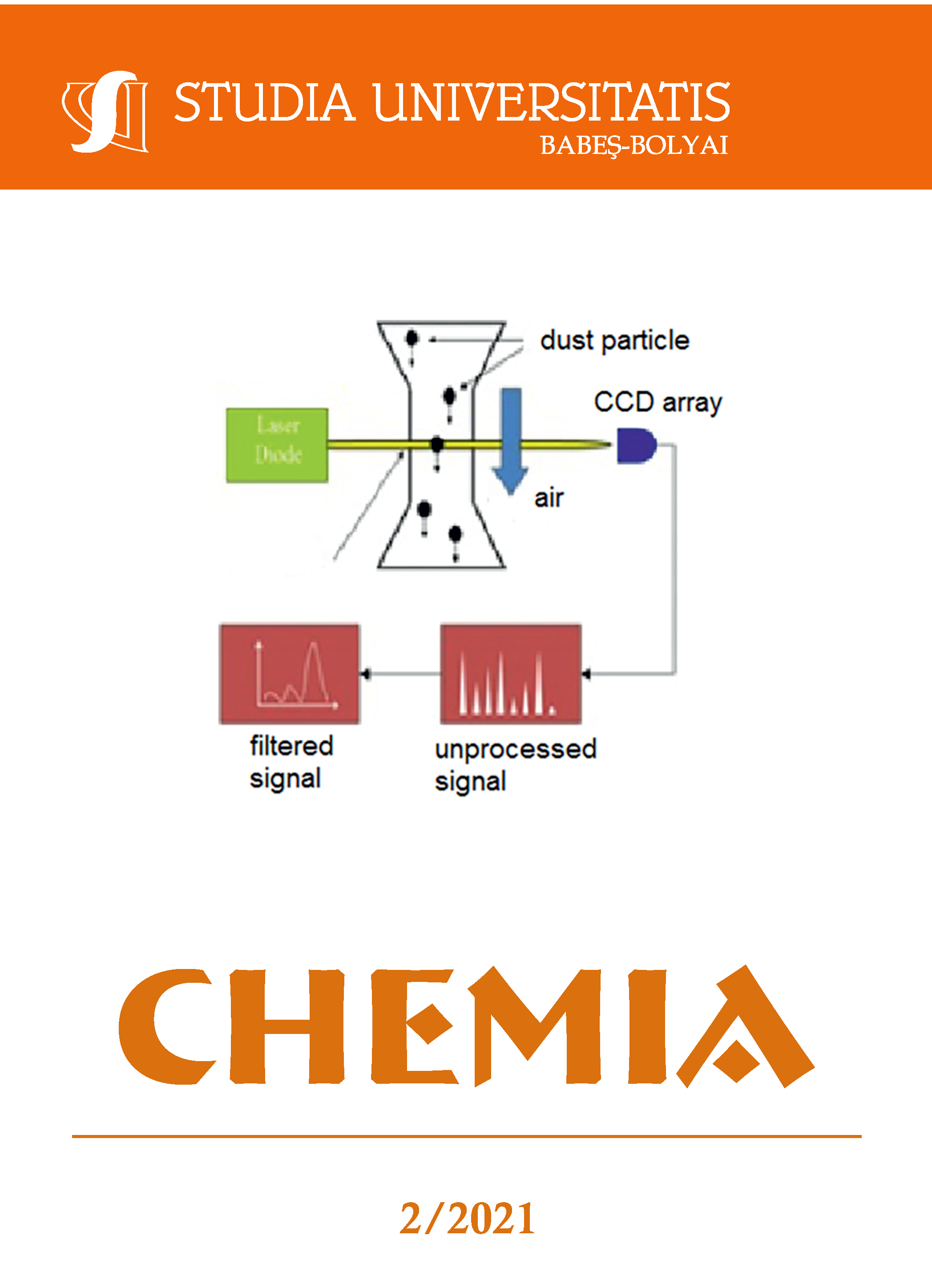
The harmful effects of airborne dust have been long known, with numerous studies proving the danger it poses to human health. The paper presents a submicron size airborne dust particle monitoring system, built in collaboration by a laboratory equipment manufacturer and a national research and development institute. The system is designed for the automotive industry, the printed circuit board production lines, and the environmental monitoring. It can measure and record data continuously and the loss of the supply voltage does not lead to the loss of the monitoring history. The key element is the particle sensor itself, consisting of a laser diode assembly - CCD area, a suction pump with continuous operation, with constant electronically controlled flow and an electro-optical detector. The system is designed with the following specifications: the applicable particle size: 0.3 μm; 0.5 μm; 1.0 μm; sampling time: 1…599 sec; programmable (25 sec. by default); average count setting: 2; 4; 8; 16; 32; 64; ambient temperature range: operating at 40ºC; power: 220V / 50 Hz; power consumption: max. 25 VA; ABS housing, IP rating 54; dimensions (L x W x D): 260 x220 x 156 mm; weight: approximately 2.5 kg.References
*** https://www.epa.gov/pm-pollution, online source accessed in 08 January 2021.
C.A. Pope, Inhal. Toxicol., 2007, 19, 33-38. doi.org/10.1080/08958370701492961
C.A. Pope, D.W. Dockery, J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc., 2006, 56, 709-742. doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2006.10464485
C.A. Pope, R.T. Burnett, M.C. Turner, Environ. Health Perspect., 2011, 119, 1616–1621. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1103639
R. Zhang, G. Wang, S. Guo., M.L. Zamora, Q. Ying, Y. Lin, W. Wang, M. Hu, Y. Wang, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 3803–3855. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00067
P. Kumar, A. Robins, S. Vardoulakis, R. Britter, Atmos. Environ, 2010, 44, 5035–5052. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.08.016
P. Paasonen, M. Peltola, J. Kontkanen, H. Junninen, V.M. Kerminen, M. Kulmala, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2018, 18, 12085–12103. doi: 10.5194/acp-18-12085-2018
M. Manigrasso, M. Vitali, C. Protano, P. Avino, Environ. Int., 2018, 118, 134-145.
C. Nguyen, L. Q. Li, C.A. Sen, E. Ronquillo, Y.F. Zhu, Atmos. Environ., 2019, 211, 159–169.
M.R. Heal, P. Kumar, R. Harrison, Chem. Soc., 2012, 41, 6606. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs35076a
*** US - EPA, National Ambient Air Quality Standards for Particulate Matter; Final Rule. Federal Register 78, 2013,10, 3086–3287.
*** WHO, Review of evidence on health aspects of air pollution – REVIHAAP Project. Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013, https://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets
*** Joint Research Centre. Particle Measurement Programme (PMP): Inter-laboratory correlation exercise with Condensation Particle Counters (CPCs). 2018, (Publications Office of the European Union).
B. Giechaskiel, B. Combust. Engines, 2018, 174, 3–16.
*** https://www.health.ny.gov/environmental/indoors/air/pmq_a.htm, online source accessed in 08 January 2021.
H.-S. Kwon, M. H. Ryu, C. Carlsten, Experim. Mol. Med., 2020, 52, 318–328.
*** https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/policies/clean-air/
*** ISO 14644:2019, Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments, www.iso.org/iso/foreword.htm
*** ISO 14698-1:2003, Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments — Biocontamination control — Part 1: General principles and methods, https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:14698:-1:ed-1:v1:en
*** Omron Corporation-Instruction Sheet for Zn-PDA air particle sensor, https://www.omron.com/global/en/
*** Omron Corporation-Instruction Sheet for air particle amplifier unit, https://www.omron.com/global/en/
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Studia Universitatis Babeș-Bolyai Chemia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.